category
Cohesion metrics measure how well the methods of a class are related to each other. A cohesive class performs one function while a non-cohesive class performs two or more unrelated functions. A non-cohesive class may need to be restructured into two or more smaller classes.
High cohesion is desirable since it promotes encapsulation. As a drawback, a highly cohesive class has high coupling between the methods of the class, which in turn indicates high testing effort for that class.
Low cohesion indicates inappropriate design and high complexity. It has also been found to indicate a high likelihood of errors. The class should probably be split into two or more smaller classes.
There are several Lack of Cohesion of Methods metrics: LCOM1, LCOM2, LCOM3 and LCOM4. We recommend the use of LCOM4 for ObjectScript systems.
LCOM4 (Hitz & Montazeri) recommended metric
LCOM4 measures the number of "connected components" in a class. A connected component is a set of related methods (and class-level variables). There should be only one such a component in each class. If there are 2 or more components, the class should be split into so many smaller classes.
In some cases, a value that exceeds 1 does not make sense to split the class if implementing a form or web page as it would affect the user interface of your program. The explanation is that they store information in the underlying object that may be not directly using in the class itself.
Method of calculation
Methods A and B are related if:
- they both access the same class-level variable, or
- A calls B, or B calls A.
After determining the related methods, we draw a graph linking the related methods to each other. LCOM4 equals the number of connected groups of methods.
- LCOM4=1 indicates a cohesive class, which is the "good" class.
- LCOM4>=2 indicates a problem. The class should be split into so many smaller classes.
- LCOM4=0 happens when there are no methods in a class. This is also a "bad" class.
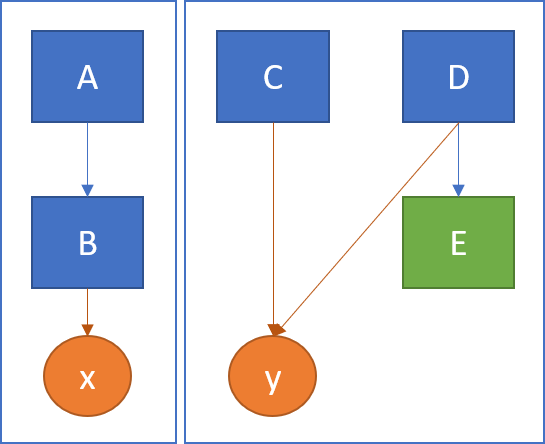
In the example below, shows a class consisting of methods A through E and variables x and y. A calls B and B accesses x. Both C and D access y. D calls E, but E doesn't access any variables. This class consists of 2 unrelated components (LCOM4=2). You could split it as {A, B, x} and {C, D, E, y}.
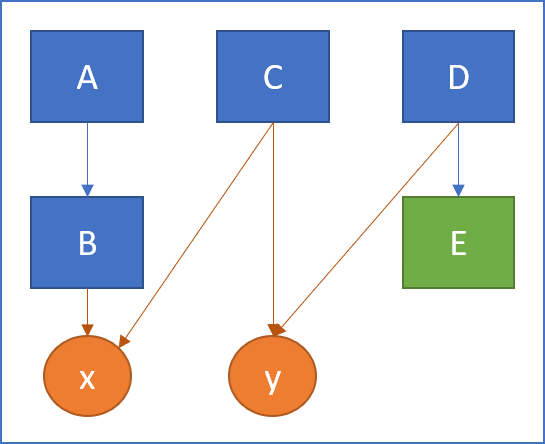
In the next example, we made C access x to increase cohesion. Now the class consists of a single component (LCOM4=1). It is a cohesive class.
In order to calculate LCOM4, we don't take into account:
- Inherited methods; they don't really own to the inspected class,
- Empty methods; they tend to increase LCOM4 as they do not access any variables or other procedures.
Links of interest
- 登录 发表评论